
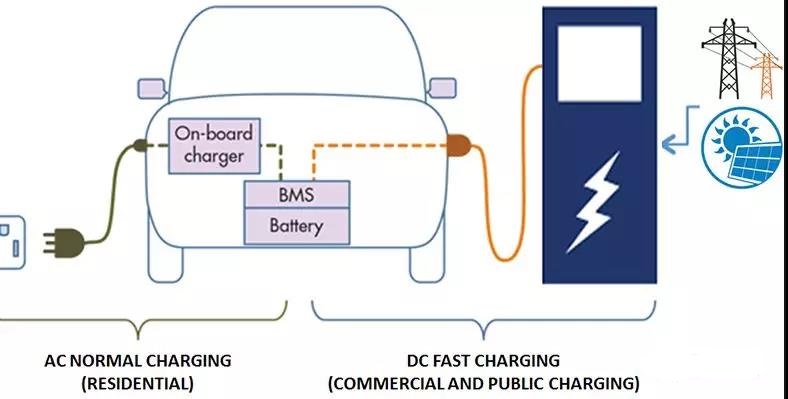
The EV charging process is delivering the power from the power grid to EV battery, no matter you are using AC charging at home or DC fast charging at shopping mall and highway. It is delivering the power from the power net to the battery for storage. Because only DC power can be stored in the battery, the AC power can not be delivered to the battery directly, it needs to be converted into DC power by the onboard charger.
Many people are worrying that the Higher power fast charging will be a huge challenge for the power grid or the low usage rate of DC fast charger. But along with the developing technology and more and more EVs on the road, faster charging would be a very rigid demand.
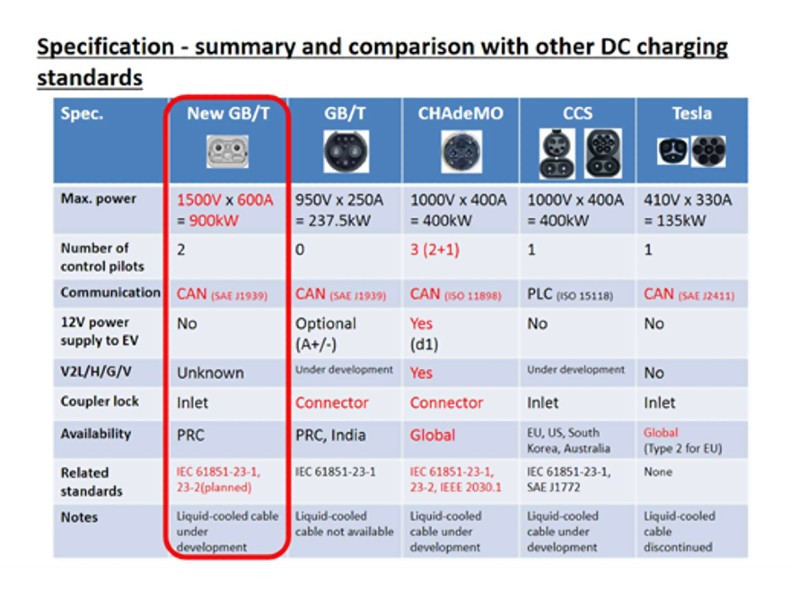
The charging standard can be divided into 5 standards, which are CHAdeMO (Japan), GB/T(China), CCS1 (US),CCS2 (EU) and Tesla. Thereinto, the communication protocol between BMS and Charger are not the same, the CHAdeMO and GB/T are adopted CAN commutation protocol; the CCS1 and CCS2 are adopted PLC communication protocols. So it is painful for the user, whose country has all kinds of charging standards EVs, who may not find the proper standard DC charging stations. In the market, ABB designed DC chargers combined two charging standards, which solved parts of the problem.
Generally speaking, DC fast charging is not to charge the battery to full within a few minutes, but to charge the car with an idea driving range in a short time, which approach the habit to drive the gasoline car. At the same time, it has a higher requirement for the safety of the battery.


