As electric vehicles (EVs) continue to gain popularity, understanding the different types of charging stations is essential for both EV owners and businesses offering charging services. EV chargers are categorized into three levels, and these three levels have many differences in different dimensions. However, in general, the higher the grade, the more power the charger outputs and the faster it charges.
In this detailed guide, we will explore the three levels of EV chargers, their characteristics, and how to choose the most suitable charging station for various needs.
Before diving into the specifics of each charger level, it’s important to understand the key factors that distinguish them:
1. Current Type: EV chargers use either alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). AC chargers are typically slower, while DC chargers provide faster charging times.
2. Input Voltage: This refers to the voltage required to operate the charger, which varies depending on the charger level and geographical location.
3. Output Power: Measured in kilowatts (kW), this indicates how much power the charger can deliver to the EV. Higher power output results in faster charging.
4. Average Charge Time: The average amount of time it takes to charge an EV battery from 0% to full. This varies based on the level of the charger, the battery capacity of the vehicle, and other factors like the vehicle’s onboard charging capabilities.
Level 1 EV Chargers: The Basic Home Solution
Level 1 chargers are the simplest and most accessible option, using a standard 120-volt AC household outlet in regions like North America. These chargers are typically provided when you purchase an EV, and they don’t require any special installation, making them a low-cost solution for EV owners.
Characteristics of Level 1 Chargers:
· Current Type: AC (Alternating Current)
· Input Voltage: 120 volts (common household outlet)
· Output Power: 1 to 1.8 kW
· Average Charge Time: 11 to 20 hours for a full charge
While these chargers are convenient for home use, they are also the slowest option. A full charge can take nearly an entire day, which may be inconvenient for users who drive frequently or have long commutes. However, Level 1 chargers are sufficient for those who have plenty of downtime, such as overnight charging, or for those who use their vehicles for short daily trips. The charging power of Level 1 is comparable to that of a common household appliance, such as a kitchen sandwich maker.
Ideal Use Case:
· Home use for occasional drivers: If you drive short distances daily and don’t need rapid charging, a Level 1 charger might be sufficient.
· Low-cost, no-installation option: Since most Level 1 chargers come with the vehicle and plug directly into a standard outlet, there’s no need for additional installation or electrical work.
Level 2 EV Chargers: The Efficient Choice for Homes and Businesses
Level 2 chargers represent a significant upgrade in terms of charging speed and power output. They operate at higher voltages than Level 1 chargers, typically using 208/240 volts in North America, and 230 to 400 volts in Europe, depending on whether the system is single-phase or three-phase.
Characteristics of Level 2 Chargers:
· Current Type: AC (Alternating Current)
· Input Voltage: 208/240 volts (U.S.) and 230/400 volts (Europe)
· Output Power: 3 to 19.2 kW (U.S.) and up to 22 kW (Europe)
· Average Charge Time: 3 to 8 hours for a full charge
In the United States, Level 2 chargers are commonly used in both residential and commercial settings. For residential applications, these chargers usually operate at 240 volts, while commercial locations may use 208 volts. An example of residential Level 2 chargers is the Injet Blazer Level 2 Home Charger, which is designed for fast and reliable home charging. In commercial settings, the Injet Vision EV Charger is a popular choice for providing quicker turnaround in high-traffic areas.
In Europe, Level 2 chargers often operate at 230 volts for single-phase systems or 400 volts for three-phase systems, allowing for even faster charging. These chargers can be mounted on poles or walls, making them flexible for various installation environments.
Ideal Use Case:
· Home use for daily commuters: If you need to charge your EV overnight or in a few hours, Level 2 chargers provide a much faster solution than Level 1.
· Commercial use for public or workplace charging: Level 2 chargers are well-suited for locations where people leave their vehicles parked for several hours, such as workplaces, shopping centers, and public parking lots.
Additional Features:
· Universal Connector: Most Level 2 chargers in North America come equipped with the SAE J1772 connector, making them compatible with a wide range of EV models. This standardization simplifies the process for both EV owners and businesses offering charging stations.
Direct-Current Fast Chargers (DCFC): The Ultimate in Speed and Power
Direct-current fast chargers, also known as DCFC or Level 3 chargers, are the fastest and most powerful chargers available today. Unlike Level 1 and 2 chargers that use AC, DCFC systems deliver direct current (DC) directly to the vehicle’s battery, bypassing the vehicle’s onboard AC-to-DC converter. This allows for much higher power outputs and significantly reduced charging times.
Characteristics of Level 3 Chargers:
· Current Type: DC (Direct Current)
· Input Voltage: 480-volt AC three-phase circuit (for conversion to DC)
· Output Power: 50 to 400 kW
· Average Charge Time: Charge to 80% in as little as 30 minutes
DC fast chargers are typically found at highway rest stops, EV charging stations, and other high-traffic commercial locations where fast turnaround is essential. The Injet Ampax Level 3 Fast Charging Station is a great example of a high-performance charger that delivers 60 kW to 240 kW (upgradable to 320 kW), allowing drivers to quickly recharge and continue their journey.
Ideal Use Case:
· Highway rest stops and commercial sites: Level 3 Chargers are ideal for locations where drivers need a quick top-up, such as along highways or at busy commercial centers.
· Fleet operations: Businesses with electric vehicle fleets benefit from DCFCs, as they can minimize downtime and keep vehicles on the road.
Maintenance Considerations:
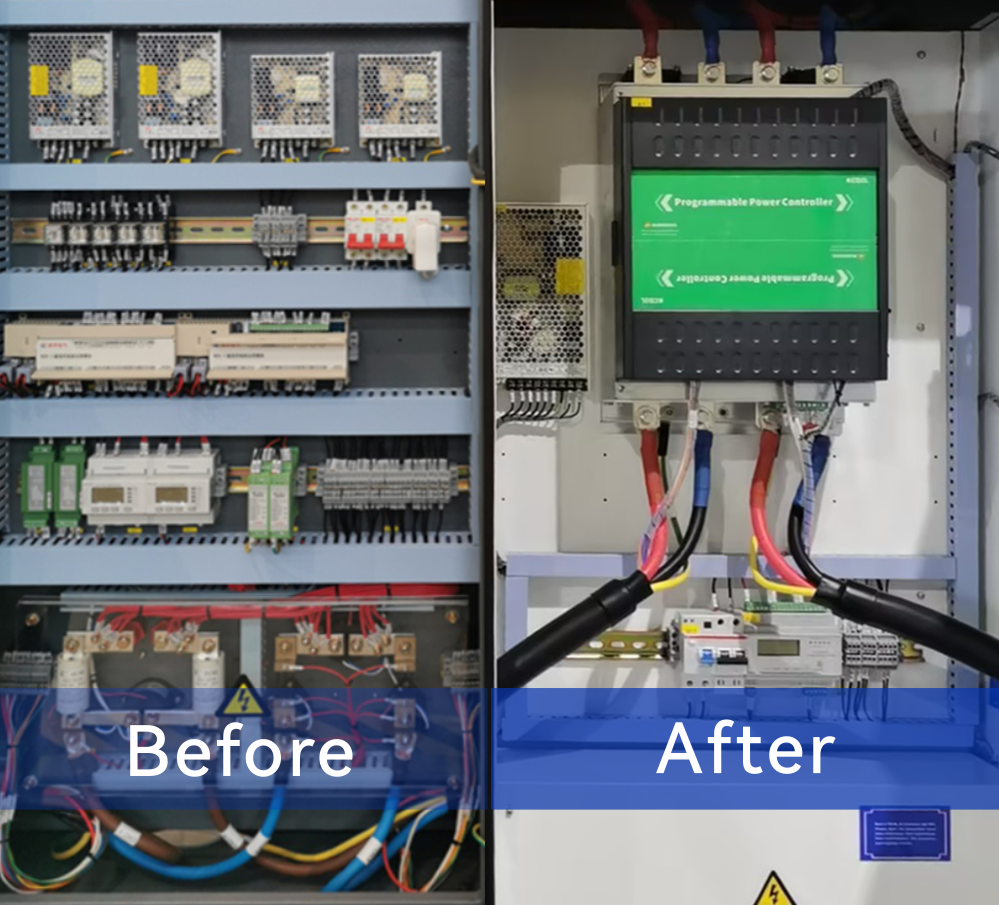
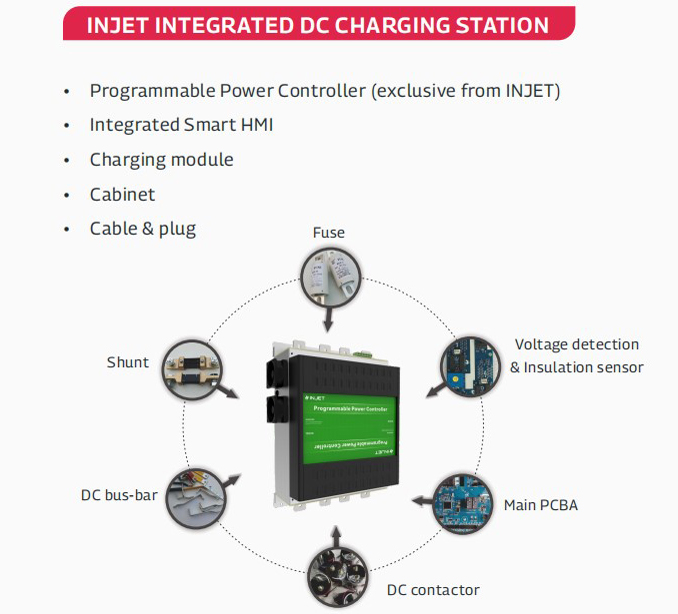
While DC fast chargers are incredibly powerful, maintaining them can be more complex than Level 1 and 2 chargers. Traditional maintenance procedures for DCFCs can take anywhere from 2 to 10 days, which may be a challenge for businesses. However, solutions like the Injet Ampax, equipped with advanced power controllers, are designed for quick and efficient repairs, with most issues resolved in less than 8 hours. (To Learn More →)
Choosing the Right EV Charging Station
Home Charging Solutions: Level 1 & Level 2
For home charging, most users will find that Level 2 chargers offer the best balance between cost and performance. These chargers deliver enough power to fully recharge an EV overnight, which is ideal for drivers who use their vehicles daily. For those who only need occasional charging or have lower daily mileage, a Level 1 charger may suffice.
Commercial Charging Solutions: Level 2 & Level 3
Businesses offering EV charging services should consider a combination of Level 2 and Level 3 chargers. Level 2 chargers are excellent for locations where vehicles are parked for extended periods, such as shopping malls, hotels, and workplaces. For high-traffic areas or highway rest stops, Level 3 chargers provide the fast charging capabilities that customers expect, allowing them to get back on the road quickly.






