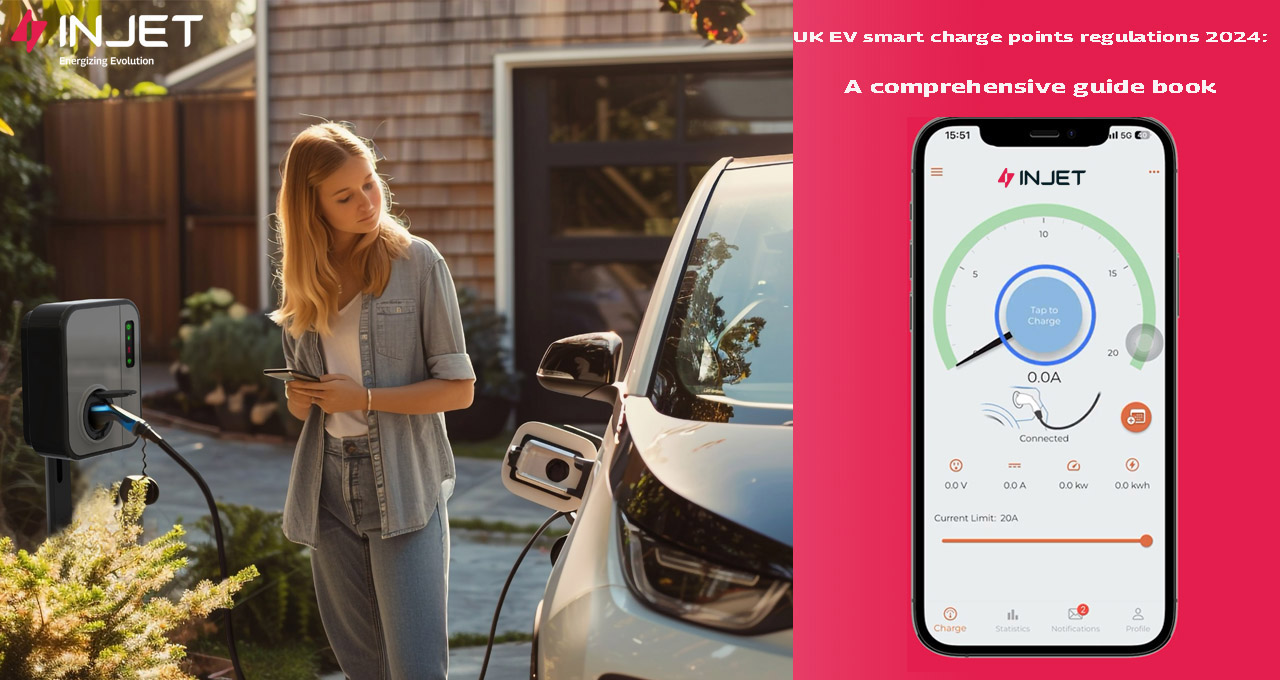
Explore More Smart Charger Solutions With Injet New Energy
Why are smart charging regulations needed?
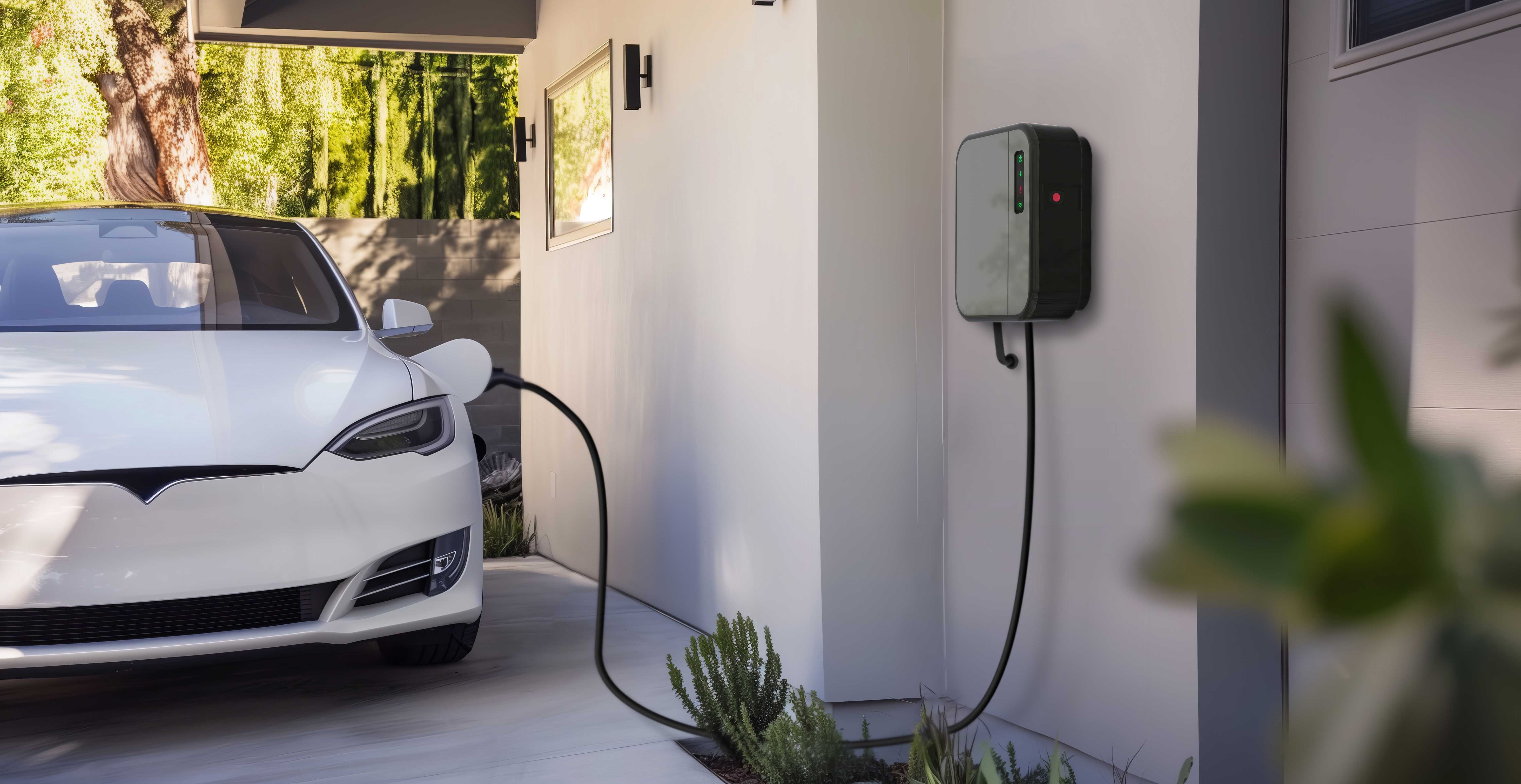
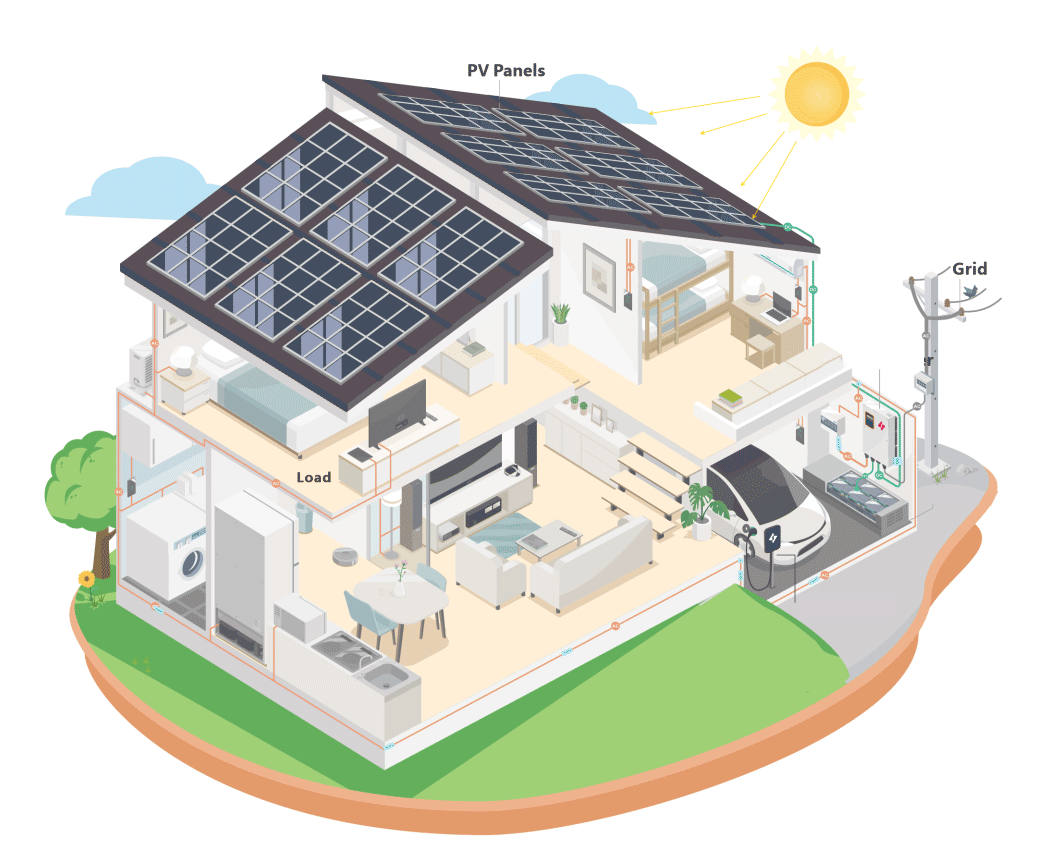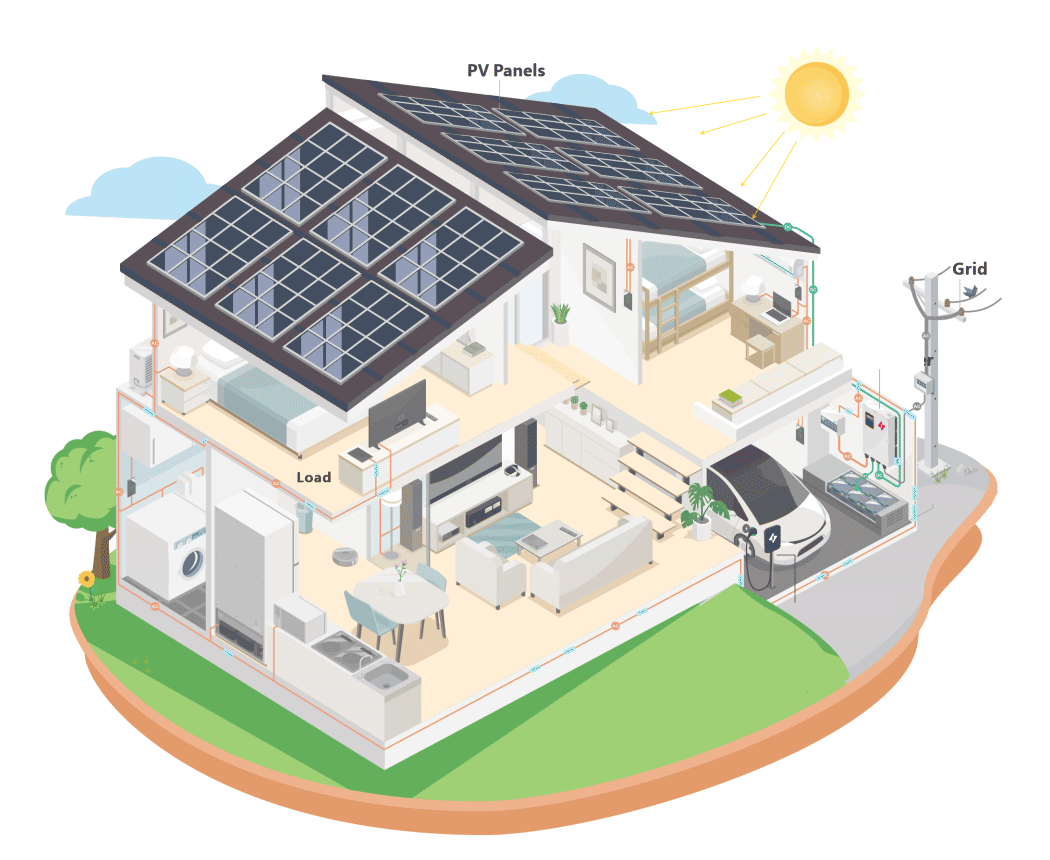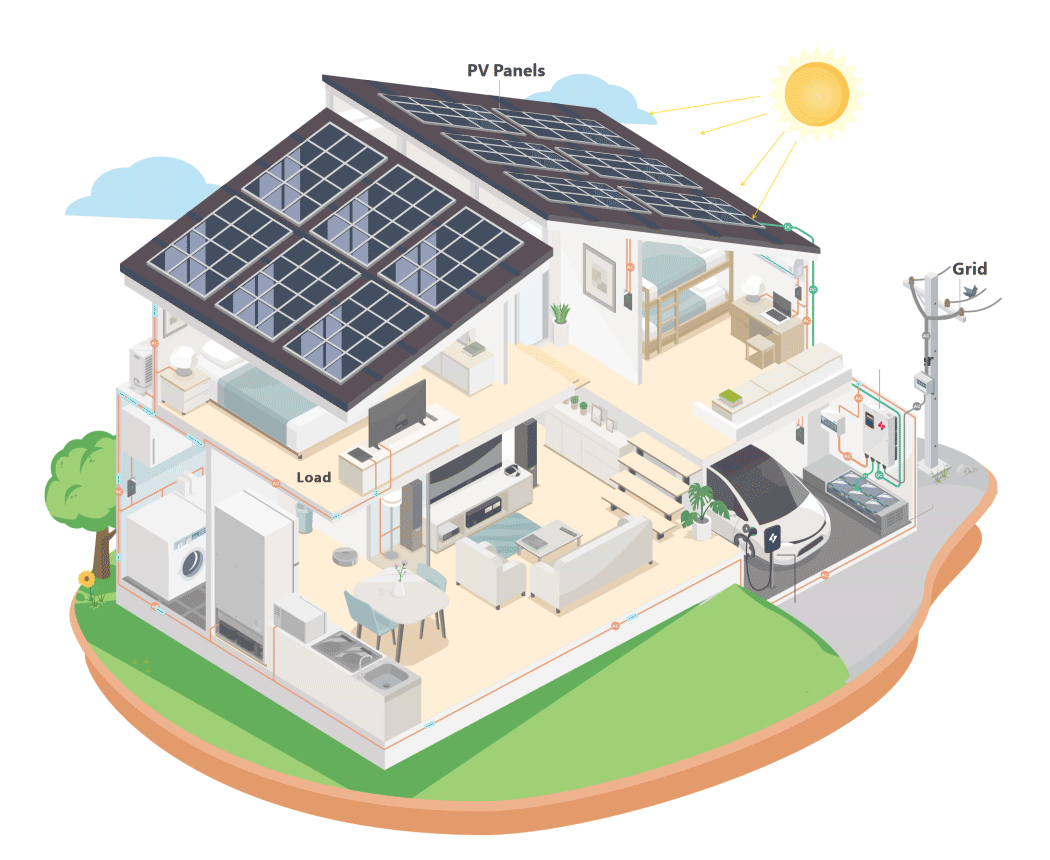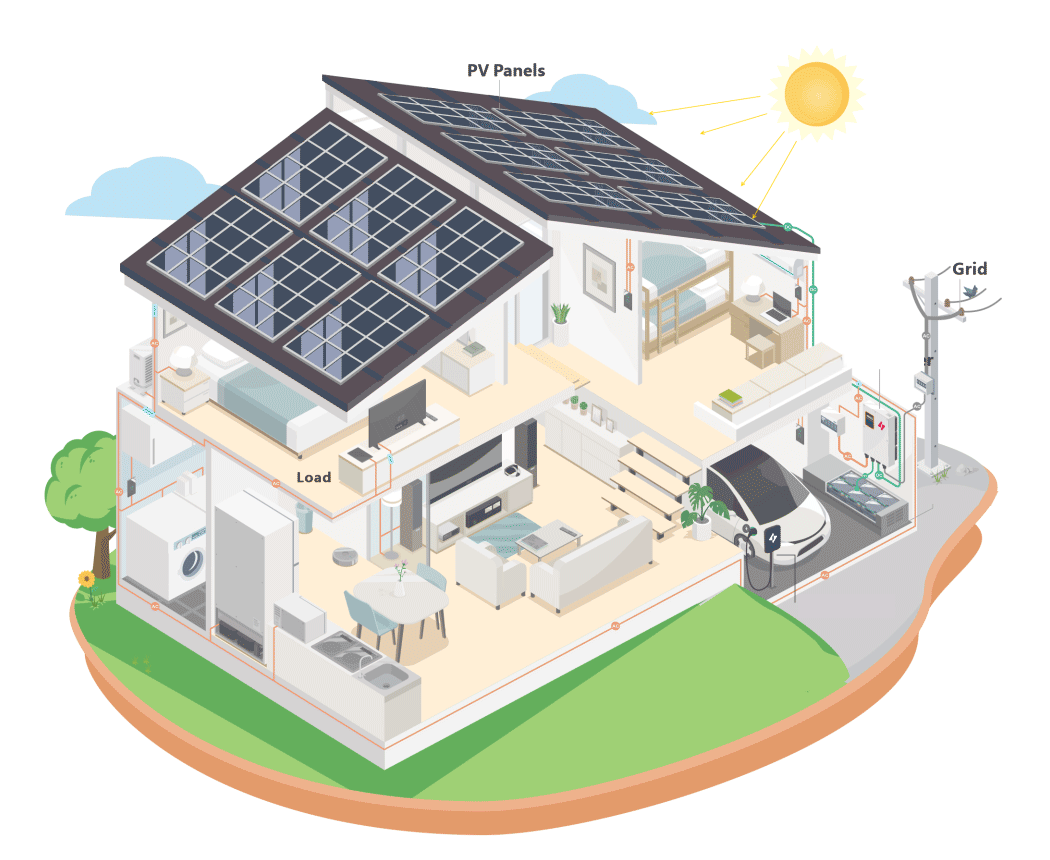
Electric vehicle charge points intended for private use in Great Britain, such as those installed at homes or workplaces, are now subject to specific regulations aimed at addressing the rising electricity demand associated with the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. These measures are designed to support the transition to a greener future while maintaining the stability of the electricity grid.
A key feature of the regulations is the requirement for smart functionality in charge points. This smart technology allows electric vehicles to be charged during off-peak periods when electricity demand on the grid is lower or when there is a greater supply of renewable energy. By doing so, it helps to optimize energy usage, reduce strain on the grid, and promote the use of sustainable power sources.
Furthermore, the smart charging regulations establish essential device-level standards to enhance the user experience and ensure safety. These standards mandate that charge points provide a minimum level of access, robust security measures, and clear, reliable information for consumers. This comprehensive approach not only supports the efficient integration of electric vehicles into the energy ecosystem but also prioritizes consumer trust and ease of use.
(Injet Eco - Smart Chargers For The UK Market)
What the Smart Charging Regulations is covered ?
The EV smart charge points regulations apply to:
· Electric vehicle private charge points: These are devices sold for use in domestic or workplace environments across Great Britain.
· Smart cables: Defined as electrical cables that function as charge points and are capable of sending and receiving information via a communications network.
The regulations do not apply to:
· Charge points sold in Northern Ireland.
· Charge points sold before 30 June 2022.
· Charge points not intended for use in Great Britain at any time.
· Charge points sold by individuals outside the scope of trade, business, craft, or profession (e.g., private second-hand sales).
· Non-smart cables or rapid charge points that do not meet the definition of smart charge points.
· Public charge points, which are subject to the Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Regulations 2017.
How the smart regulations to comply?
The Electric Vehicle smart charge points regulations state that charge points sold for the intended private charging of vehicles must meet certain device-level requirements, which include:
Smart functionality
· Capability to transmit and receive data via a communication network.
· Ability to respond to incoming data from the communication network by:
1. Adjusting the rate of electricity flow through the charge point (increasing or decreasing as needed).
2. Modifying the timing of electricity flow through the charge point.
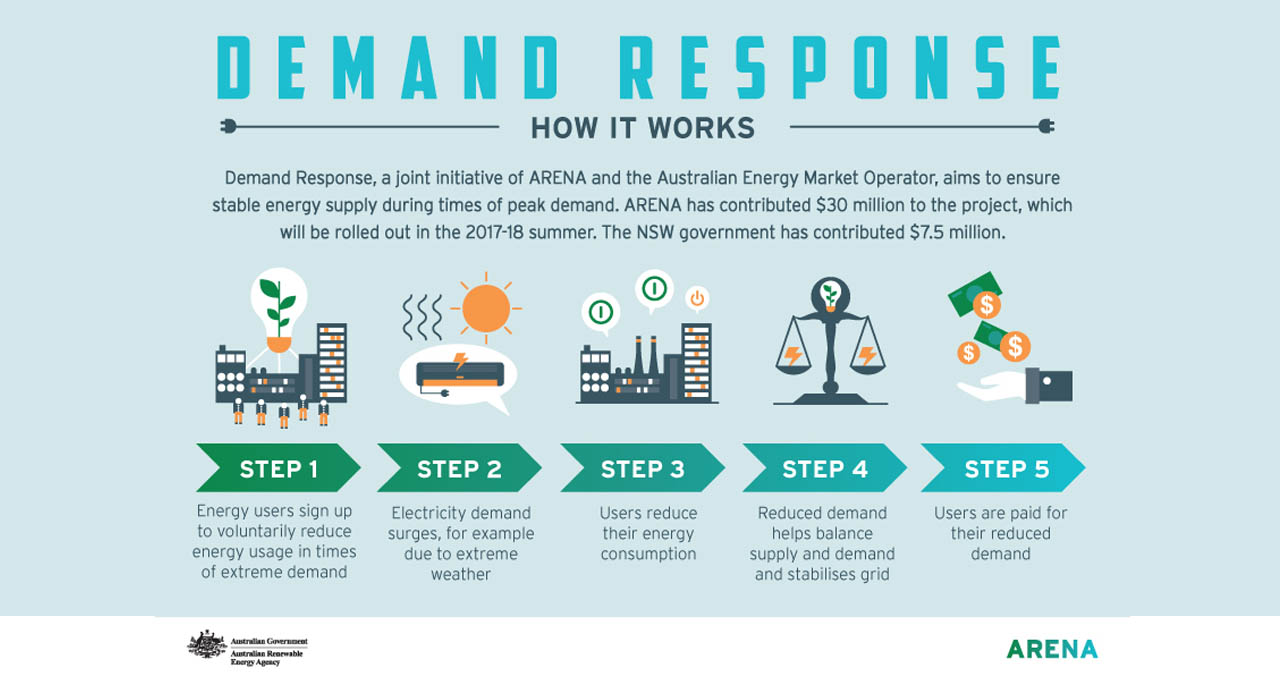
· Functionality to support demand-side response (DSR) services, including real-time DSR operations.
Note: Demand-side response (DSR) refers to adjusting electricity consumption to align with available supply. It is also known as demand-side flexibility or demand response.
· Integration of at least one user interface that allows operation of the charge point in compliance with regulations. This interface may be built into the charge point or provided separately for the owner’s access.
Electricity supplier interoperability: allowing the charge point to retain smart functionality even if the owner switches electricity supplier
To protect consumers from being locked into specific providers, a charge point must be designed to retain its smart functionality even if the owner switches electricity suppliers. This ensures the charge point’s core smart features remain fully operational, regardless of the supplier. While a change in how smart functionality is delivered is acceptable—such as requiring a new smartphone app to manage the charge point—the minimum smart functionality must always be maintained. Similarly, smart charging settings, like default charging hours, may need to be reset using the new supplier’s app, as these preferences are not expected to transfer automatically. However, the loss of any additional smart features beyond the minimum requirements specified in the Regulations is permissible. Crucially, switching electricity suppliers should never require the owner to purchase a new charge point to continue using smart charging features.
Loss of Communications Network Access
To enable smart functionality, charge points depend on a communication network such as Cellular, Ethernet, or Wi-Fi to transmit and receive signals. It is essential that charge points are designed to continue charging an EV even if network connectivity is lost, ensuring vehicle owners can still charge their cars without interruption. While the Smart Regulations do not mandate specific operational measures for charge points during a loss of connection, they do require the ability to charge an EV to be maintained. One possible way to meet this requirement is by adhering to the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) EN 303 645.
Safety Measures: Ensuring that users are prevented from performing operations that could pose a risk to personal health or safety.
· Charge points must be designed or configured to prevent owners or other end-users from carrying out certain actions that could jeopardize their own safety or that of others.
· The regulations introduce additional safety requirements specifically related to smart functionality. These requirements mandate that safety must take precedence over the following operations:
· Overriding the default charging mode during designated hours.
· Disabling the provision of demand-side response services.
· Bypassing the random delay feature.
A measuring system
A charging system must measure or calculate the electricity imported or exported and the duration of the charging session, ensuring this information is accessible to the owner.
The charge point should monitor energy consumption data and provide owners with a way to view details from the previous 12 months. This aims to inform consumers about their electricity usage. The data can be obtained either through direct measurement (e.g., a meter within the charge point) or through calculations. Owners must be able to access this information via a user interface. The format and location of the interface are flexible, with options including physical displays on the charge point, mobile applications, or web-based platforms.
All data provided must be accurate within a 10% margin of error, with no systemic inaccuracies—meaning errors caused by the charge point’s design or manufacturing must not be consistent or predictable.
Additionally, a charge point must have the capability to measure or calculate the electrical power imported or exported in watts or kilowatts every second. This information must be deliverable through a communications network. Such capabilities are intended to facilitate participation in Demand Side Response (DSR) services, should the owner choose to engage in them.
Security
Security requirements consistent with the existing cyber security standard ETSI EN 303 645
In addition to these points, the Electric Vehicle Smart charge points regulations likewise require that charging points meet the following criteria:
Off-Peak Charging Setup
· Charge points must come pre-configured with default charging hours set during off-peak periods.
· Owners must be provided with the option to accept, modify, or disable these default settings during initial setup and at any time afterward.
Randomised Delay Functionality
· Ensuring grid stability is a central goal of the Government’s smart charging policies. A potential challenge arises when multiple charge points begin charging or adjust their charging rates simultaneously—such as after a power outage or in response to an external signal like a Time-of-Use (ToU) tariff. Such synchronized actions could create demand surges or drops, potentially destabilizing the grid.
· To address this, the regulations mandate the inclusion of randomised delay functionality. By introducing a randomised offset, this feature helps distribute electricity demand more evenly over time, allowing for a gradual increase in load that is easier for the grid to manage.
What can Injet New Energy do for you under the Smart Charge Regulations UK?
Injet New Energy is dedicated to advancing the global transition to clean energy and making a meaningful impact on the renewable energy industry. The UK market has always been one of our key strategic priorities. Recently, our team traveled to the UK to participate in the 2024 London EV Show, where we engaged with international teams and showcased our innovative products.
With the UK market as a key focus of our strategic growth, we’ve developed the Injet Eco, a cutting-edge AC EV charger tailored specifically for local needs. Fully compliant with the EV Smart Charge Points Regulations, the Injet Eco has achieved UKCA and CE certifications, ensuring safety, reliability, and efficiency for diverse applications.
Key Features:
APPEARANCE STRUCTURE
· Palette Design: Blends perfectly into any installation environment with its versatile aesthetic.
· Flexible Configuration: Tethered or Untethered designs to meet diverse user needs.
· Push-to-Install Convenience: Effortless installation and worry-free after-sales support.
· LED Status Indicators: At-a-glance visibility of charging status.
INTERNAL COMPONENTS
· Smart Linux System: Supports a wide array of features (Pro/Pro Plus models).
· Integrated Leakage Detection: AC 30mA/DC 6mA, eliminating the need for costly Type B leakage protection switches.
· Built-in PEN Design: Saves on the expense of additional grounding rod installations.
· Electronic Lock Mechanism: Ensures the charging cable cannot be removed during use, enhancing safety.
· Multiple Version Options: Catering to various project budgets with Smart, Pro, and Pro Plus versions.
· Wi-Fi 6 Module: Supports 2.4GHz & 5GHz communication for safer, faster, and more stable data transmission.
· Optional 4G Connectivity: Offers diverse networking solutions to clients.
SCENARIOS
· Residential Use: Connects with energy management systems to utilize surplus solar power for charging.
· Semi-Public Use: Power-sharing across multiple units.
· Commercial Use: Interfaces with POS machines and MID meters to meet commercial requirements.
Join us in transforming the UK’s renewable energy landscape. Contact our team to discover how the Injet Eco can meet all your smart charging needs!