Introduction
Electric vehicles (EVs) have been gaining popularity in recent years, as people become more environmentally conscious and seek to reduce their carbon footprint. However, one of the major challenges facing the widespread adoption of EVs is the availability of charging infrastructure. As such, the development of EV charging technology is crucial in ensuring that EVs become a viable option for the average consumer. In this article, we will explore the future of EV charging technology, including advancements in charging speeds, charging stations, and wireless charging.
Charging Speeds
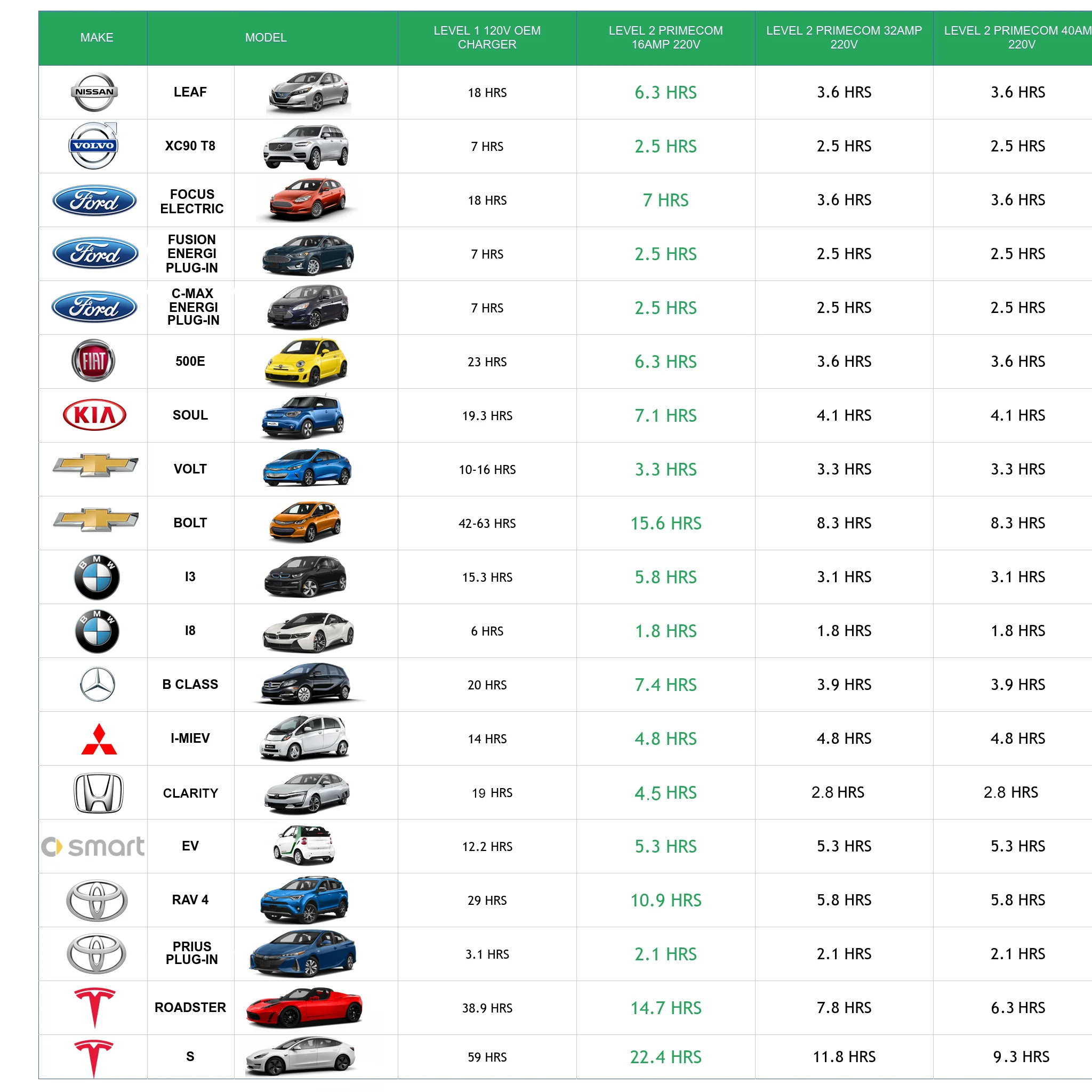
One of the most significant advancements in EV charging technology is the improvement in charging speeds. Currently, most EVs are charged using Level 2 chargers, which can take anywhere from 4-8 hours to fully charge a vehicle, depending on the battery size. However, new charging technologies are being developed that can drastically reduce charging times.
The most promising of these technologies is DC fast charging, which can charge an EV up to 80% in as little as 20-30 minutes. DC fast chargers use direct current (DC) to charge the battery, which allows for much faster charging speeds than the alternating current (AC) used in Level 2 chargers. Additionally, new battery technologies are being developed that can handle faster charging speeds without compromising the lifespan of the battery.
Another promising technology is ultra-fast charging, which can charge an EV up to 80% in as little as 10-15 minutes. Ultra-fast chargers use even higher levels of DC voltage than DC fast chargers, which can deliver up to 350 kW of power. However, ultra-fast chargers are still in the early stages of development, and there are concerns about the impact of such high charging speeds on the lifespan of the battery.
Charging Stations
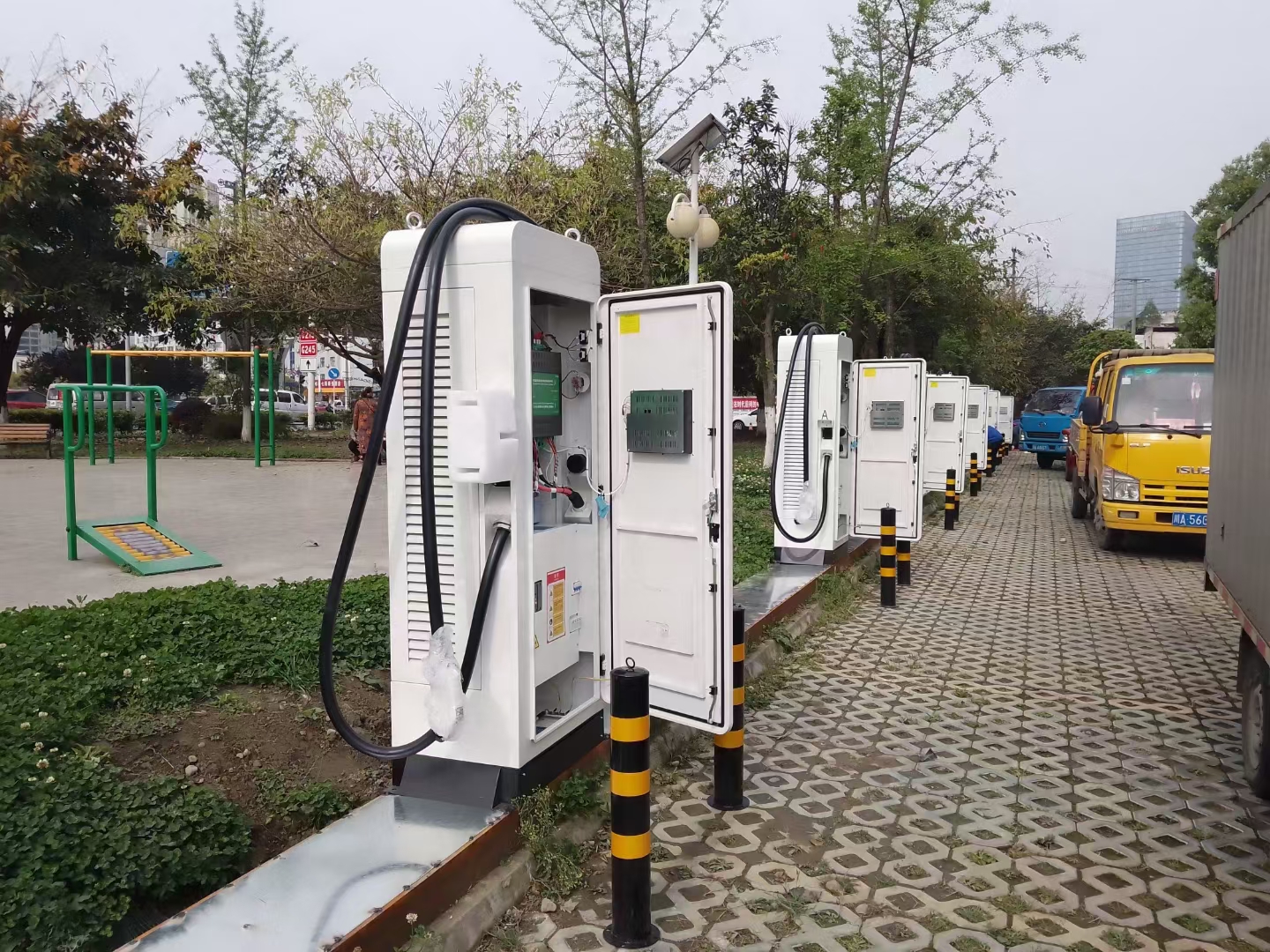

As EV adoption continues to increase, so too does the need for more charging stations. One of the biggest challenges facing the development of EV charging infrastructure is the cost of installing and maintaining charging stations. However, there are several new technologies that can help reduce these costs and make charging stations more accessible.
One such technology is modular charging stations, which can be easily assembled and disassembled as needed. These charging stations can be installed in a variety of locations, including parking lots, public spaces, and even residential areas. Additionally, modular charging stations can be equipped with solar panels and battery storage systems, which can help reduce their reliance on the grid.
Another promising technology is vehicle-to-grid (V2G) charging, which allows EVs to not only consume energy from the grid but also return energy back to the grid. This technology can help reduce the strain on the grid during peak demand hours and can even allow EV owners to earn money by selling energy back to the grid. Additionally, V2G charging can help make charging stations more profitable, which can encourage more investment in charging infrastructure.
Wireless Charging
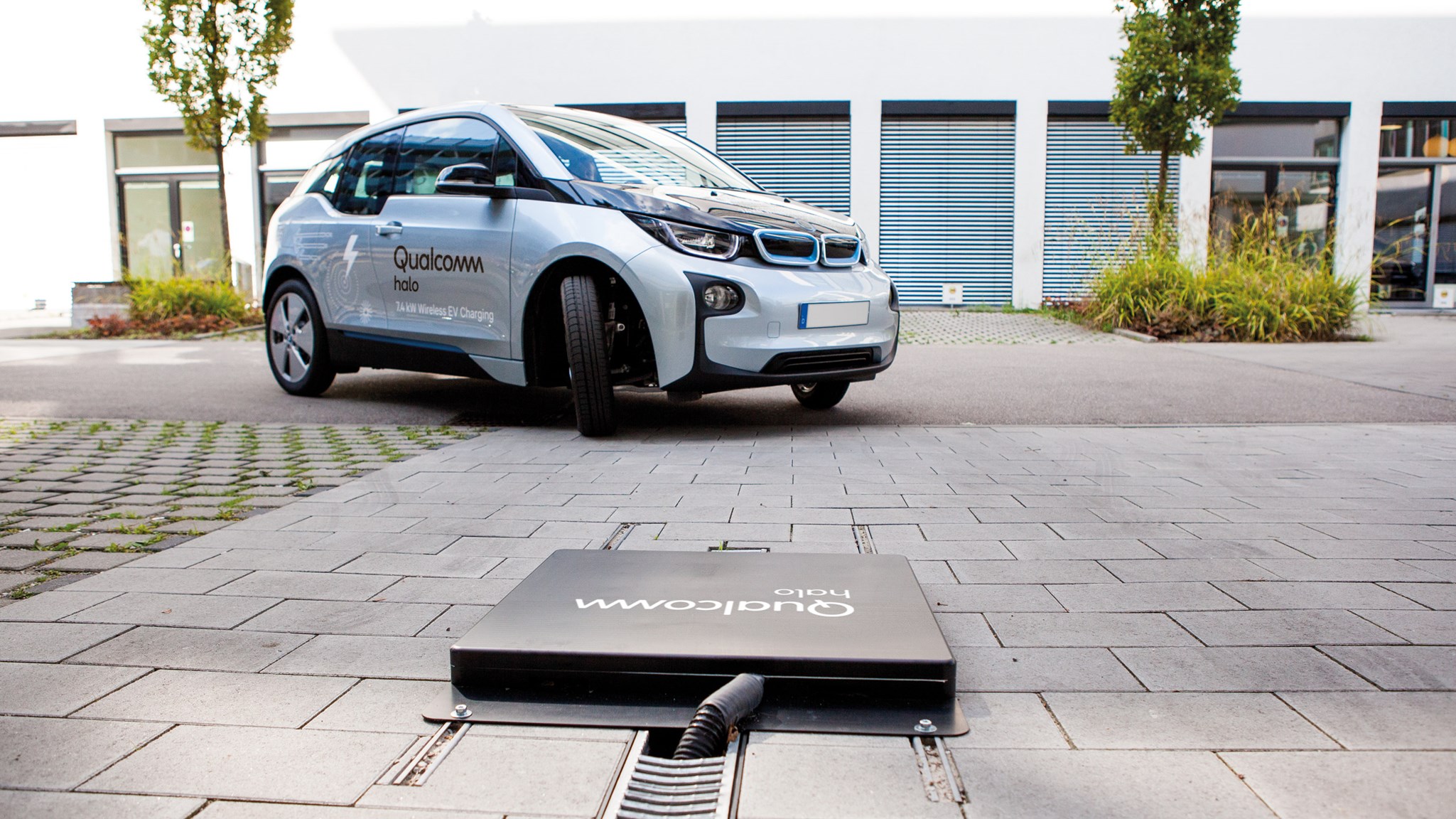

Another area of innovation in EV charging technology is wireless charging. Wireless charging, also known as inductive charging, uses electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between two objects. This technology is already being used in a variety of applications, including smartphones and electric toothbrushes, and is now being developed for use in EVs.
Wireless charging for EVs works by placing a charging pad on the ground and a receiving pad on the underside of the vehicle. The pads use electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between them, which can charge the vehicle without the need for cables or physical contact. While wireless charging is still in the early stages of development, it has the potential to revolutionize the way we charge our EVs.
Conclusion
The future of EV charging technology is bright, with many advancements on the horizon that will make charging faster, more accessible, and more convenient. As EV adoption continues to increase, the demand for charging infrastructure will only
- Previous: Smart and Connected EV Chargers
- Next: The benefits of using an EV charger
