Injet is going to show you the basic electric vehicle (EV) terms related to voltage, current, power (kilowatts), and energy (kilowatt hours). It's helpful for those new to EVs or seeking a best ev charging solution.
Key Units of EV Charging Measurement
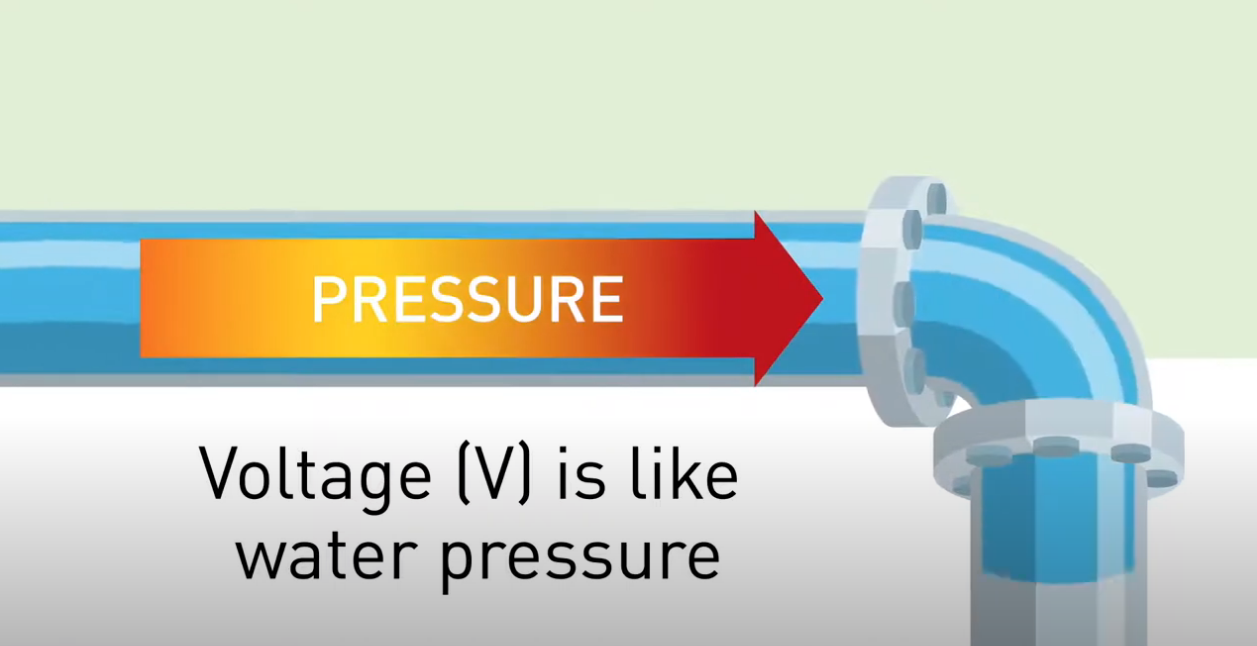
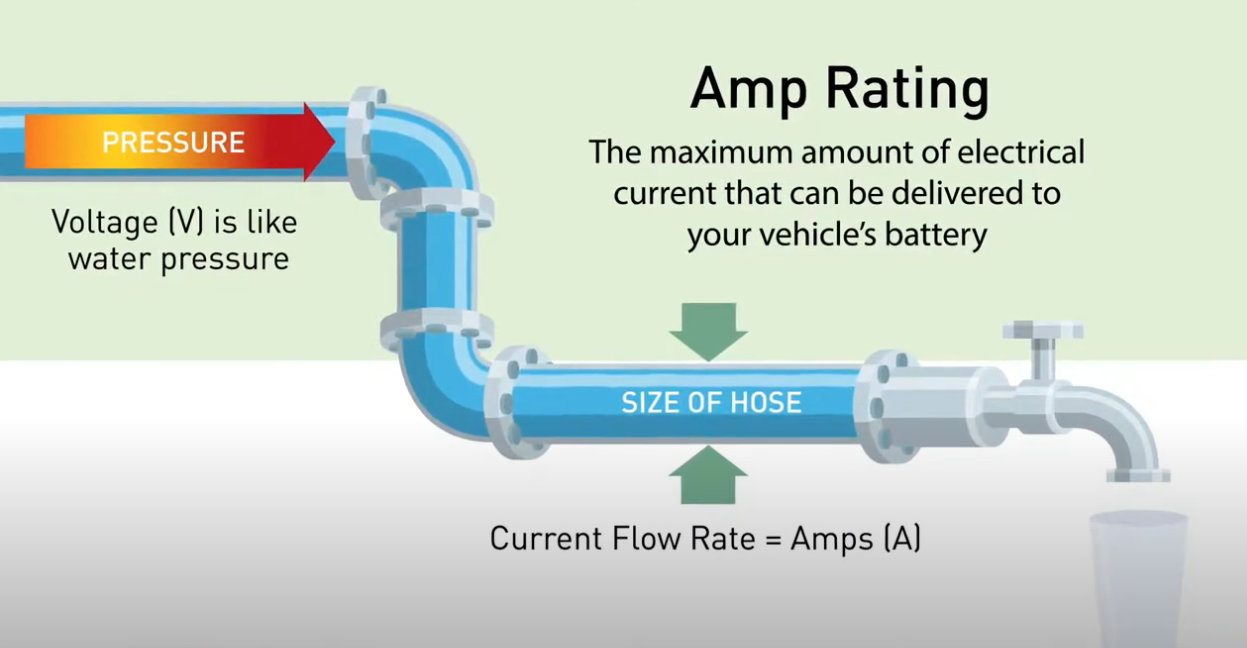
• Voltage (Volts): It measures the electrical force or pressure in an electric circuit. Think of it like the height of water in a tower, creating pressure.
pushing electrical current (amps) through the system. The power delivered to an EV is measured in kilowatts (volts x amps).
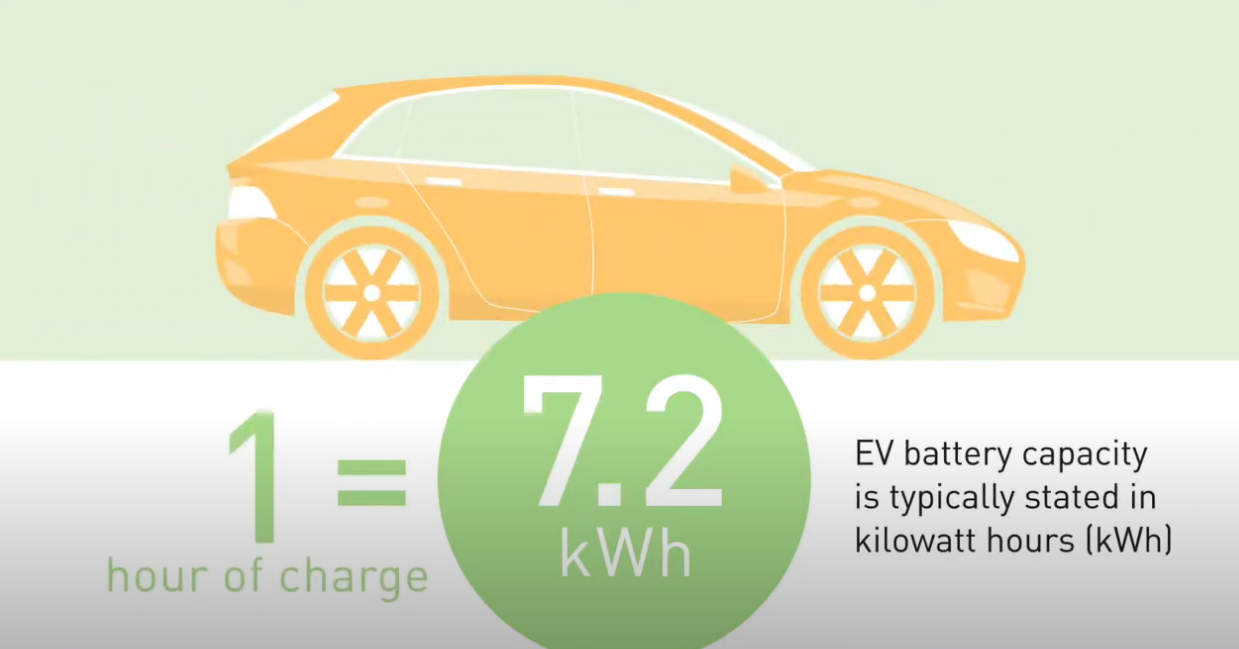
In a charging station, the voltage (like water pressure) pushes electrical current (amps) through a circuit, delivering power. A station rated at 240 volts and 30 amps means it delivers power at 7.2 kilowatts (240V x 30A ÷ 1000).
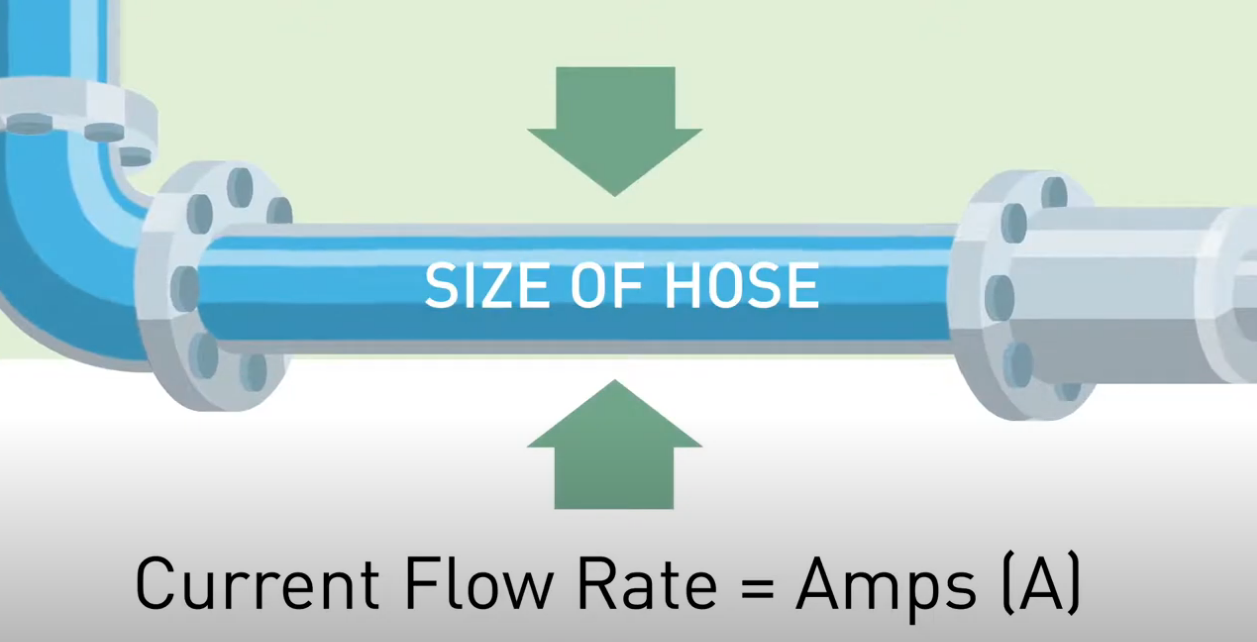
• Current (Amps): Measures the volume or flow rate of the electric current. The flow of electricity at a point in a circuit, just like the water flowing through a pipe.
• Power (Kilowatts): Measured as voltage multiplied by current, which means the kilowatt value listed in the charging station specifications is the rate at which your vehicle will charge to determine how much power will flow to your car's battery.
A unit of power equal to 1,000 watts, calculated as volts multiplied by amps (e.g., 240 volts x 30 amps = 7.2 kW).
Kilowatts indicate the amount of energy work performed over time.
• Energy (Kilowatt hours): A measurement of how much power is used or stored over time, it representing the use of one kilowatt of power for one hour.
for example a 240 volt level 2 charging station with a 30 amp rating will supply 7.2 kilowatts per hour after one hour of charging your ev, it has added 7.2 kilowatt hours of energy to your vehicle.
Understanding the Language of EV Charging
Imagine electricity flowing into your car like water in a plumbing system. The voltage, measured in volts, acts like water pressure, pushing the electrical current. The current flow, measured in amps, is similar to the water's volume.
EV charging stations are rated by a combination of these units: kilowatts (kW), volts, and amps.
Decoding the Ratings: KW = Charging Speed
The kilowatt (kW) value listed on a charging station indicates the rate at which your vehicle will charge. To calculate the power delivered to your car's battery, multiply the volts by the amps and divide by 1,000. For example, a 240-volt Level 2 station with a 30-amp rating delivers 7.2 kW per hour.
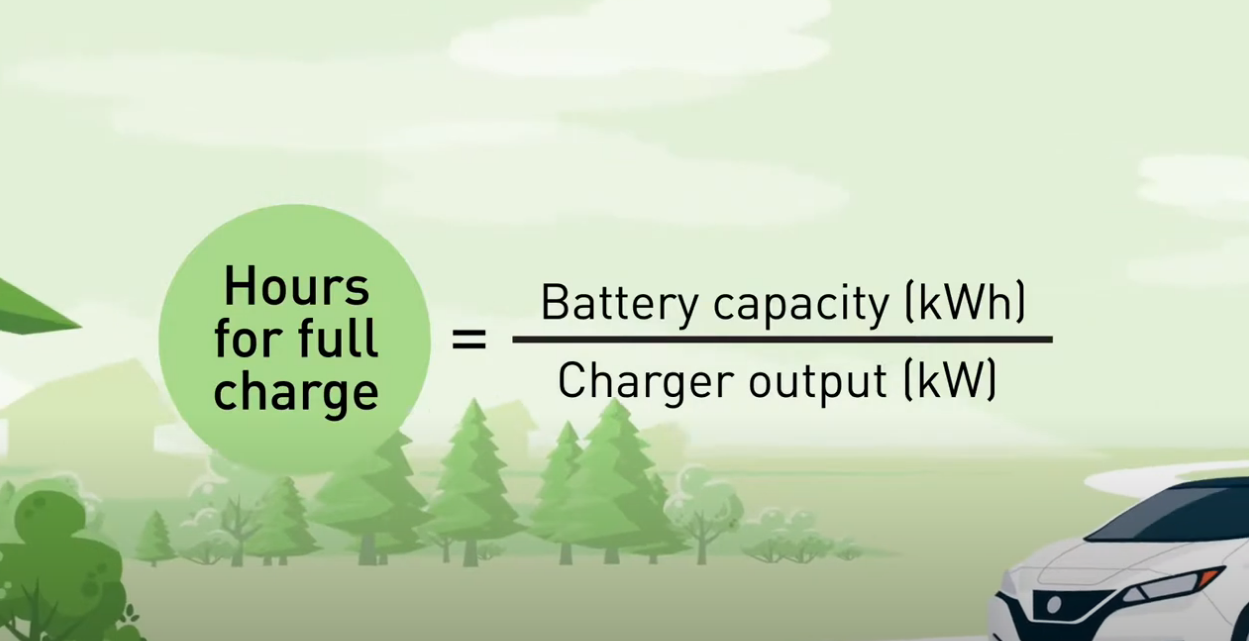
Estimating Charging Time: Battery Capacity Matters
Knowing the charging station's kW output allows you to estimate charging time for your car. Simply divide your vehicle's battery capacity (in kilowatt-hours, kWh) by the charging station's kW output.
Let's say your EV has a 42 kWh battery and is plugged into a 7.2 kW station. A full charge would take approximately six hours.
Important Note: Each EV also has a maximum charge rate, which is the amount of power its battery can safely accept. This might be lower than the charging station's output. Consult your owner's manual or search online to find this value.
Choosing the Right Charger for You
Several factors influence your ideal charging station amperage:
• Average Daily Mileage: How many miles do you typically drive per day?
• Home Charging Frequency: Can you charge at home regularly?
• Vehicle's Charging Rate: How much power can your car's battery handle?
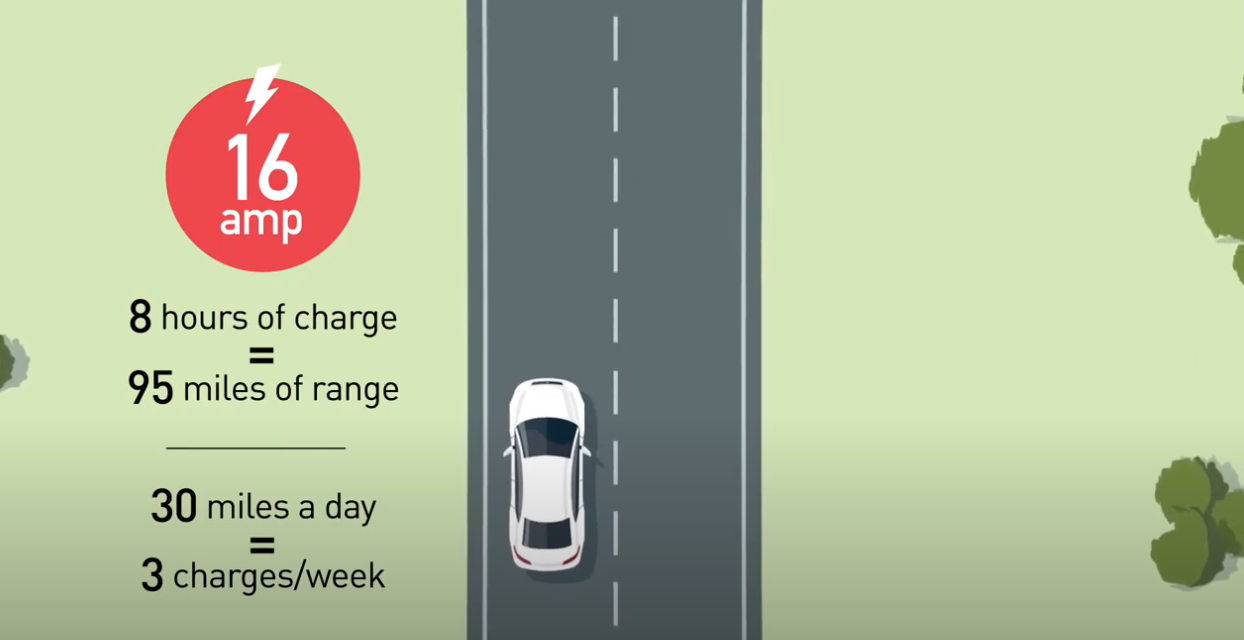
For example, using a 16-amp station for eight hours provides roughly 95 miles of range per charge. If you drive 30 miles daily, you'd only need to charge overnight three times a week. For longer commutes, consider a higher amp station for fewer weekly charges.
Planning for the Future Charging Experience
Think ahead! Consider potential changes like:
• Transitioning to a fully electric vehicle from a plug-in hybrid.
• Owning multiple EVs.
• Adjustments to your driving habits.
A higher amp station might be wise if you anticipate needing faster charging in the future.
Ready to Choose Your EV and Charger?
Injet can provide a complete charging solution, we provide services for homes, offices, charging stations and fleets, our stable and high-quality charging products will bring you the ultimate electric vehicle charging experience.